IRT, in collaboration with the EBU and BBC, is engaged in the study to evaluate and potentially enhance LTE-based 5G Terrestrial Broadcasting. We are evaluating this technology so that it can meet requirement for terrestrial broadcasting in static and high-speed environments.

The study item description is contained in document RP-181342. During Rel-14, the use cases and scenarios for eMBMS services based on LTE have been expanded to include terrestrial broadcasting. Among others, LTE supports dedicated eMBMS deployments with larger intersite distance (by the introduction of new cyclic prefix of 200us), and other aspects such as network sharing (the same broadcast content can be shared by multiple operators) and receive-only mode (no need for uplink or feedback from users).
In 3GPP RAN1#94bis meeting EBU, BBC and IRT prepared two contributions focused on the relevant requirements for Terrestrial Broadcasting and the adequate methodology to evaluate different network deployments. Our contributions are public available here:
• R1-1810319 – Public service broadcaster requirements and background information relevant to LTE-based 5G Terrestrial Broadcast
• R1-1811588 – Scenarios and simulation assumptions for the LTE based terrestrial broadcast gap analysis
In 3GPP RAN1#95 it was time to present evaluation results as contained in our third contribution:
• R1-1812430 – Evaluation Results for LTE-Based 5G Terrestrial Broadcasting
Have a look at some of our findings regarding the possibility to increase cyclic prefix and OFDM symbol duration. If you are curious, more details are given in the link above.
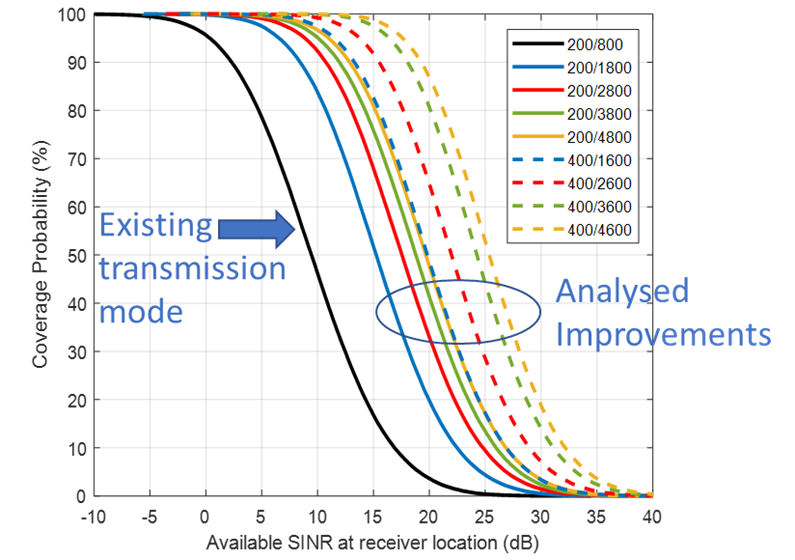
Analysis of different numerology options to improve roof-top reception in large SFN areas
With these activities, IRT continues to evaluate the potential of 5G for media distribution. Keep an eye on IRT-Lab for further news.